The Demographic Transition:
The Demographic Transition (the process of change in a society's population from a condition of high CBR and CDR and low rate of NI to a condition of low CBR), produces local variations in natural increase, fertility, and mortality.
- Stage 1: Low Growth/High Stationary: High birthrate, high death rate, steady natural increase. Most of the world's history would be placed into this stage, when people depended on hunting and gathering for food. Between 8000 BC and 1750 AD, the population grew from 5 million to 800 million caused by the agricultural revolution. Today, no country still remains in stage 1.
- Stage 2: High Growth/Early Expanding: Very high birthrate, falling death rate, and a rapid natural increase. After the agricultural revolution, the population steadily grew. After the 1750s, the Industrial Revolution resulted in industrial technology that made certain communities a healthier place to live, which led to longer life expectancies. The Medical Revolution also eliminated causes in LDCs, and decreased pandemic outbreaks.
- Stage 3: Moderate Growth/Late Expanding: Rapidly falling birthrate, slowly falling deathrate, and very slow natural increase. During the half of the 20th century, most of the western countries transitioned into stage 3. The economy plays a large role in this as well, when people begin to move into cities rather than the countryside and have less children.
- Stage 4: Low Growth/Low Stationary: Slowly falling birthrate, slight fall in deathrate, and very slow natural increase, usually the natural increase will reach zero. This condition is called zero population growth.
 |
| Demographic Transition Model (http://www.sd84.k12.id.us/clark/mike.turnlund/Current%20World%20Issues.htm) |
Population Pyramids:
A country's stage of demographic transition gives it a distinctive population structure, a bar graph called a population pyramid displays the age and gender of the population of the country.
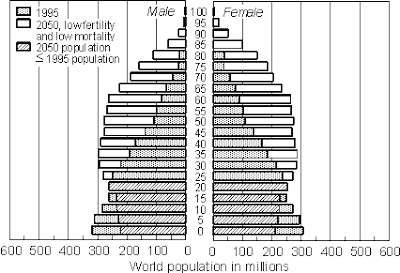 |
| The world's population pyramid |
Countries in different stages of demographic transition:
- Stage 2 (High Growth): Young people having children, rapid growth, few older people, not good for the economy.
- Stage 3 (Moderate Growth): modest growth, slower in growth, relitively more even age distrabution and sex ratio.
- Stage 4 (Low Growth): more older people due to longer life expectancy, reasonable amount of children being born, sustainable population.
Current Event: http://www.bnet.com/article/healthcare-the-upside-of-an-aging-population-plenty-of-great-jobs/404806
This article regarding the baby boomer's future retiring discusses the importance of the the relations between age distrabution and healthcare. Since this is a large sum of people who will not be working in the job force anymore, as a country and even globally, we are going to need better healthcare and more workers taking their places. This is essential to the economies of every western country and to sustain the population.
